#Research & Development
Bio-based fibers with good flame retardancy
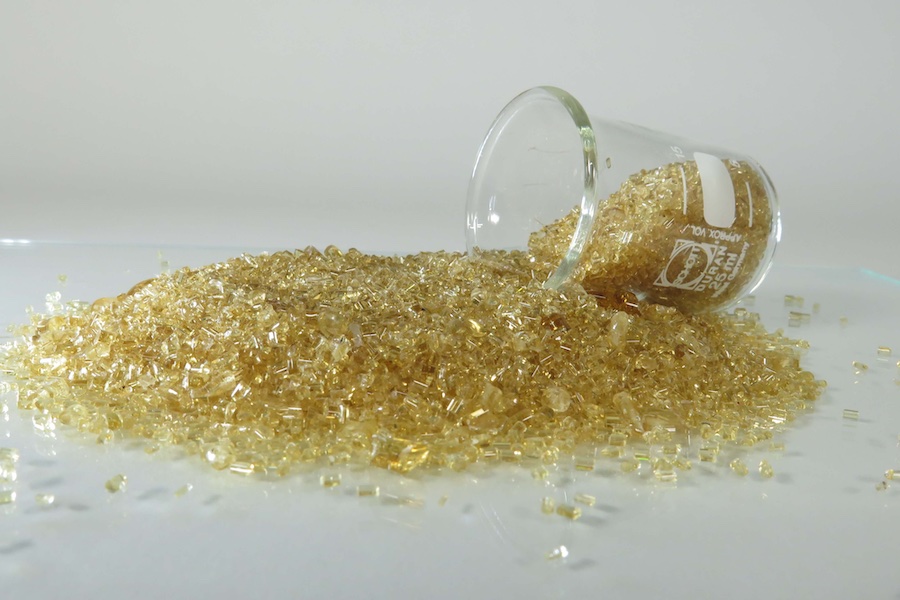

The recent fire disaster in Switzerland has revealed how crucial the use of flame-retardant materials is in construction materials, insulation, and many other everyday objects. Textiles with flame-retardant properties fulfill a particularly important function here, as they are used in considerable quantities - not only in building materials, but also in safety and protective clothing, in vehicle interiors, and in home furnishings such as carpets and upholstered furniture.
Flame-retardant compounds have been used for synthetic fibers for decades. Inorganic, brominated, or organophosphorus compounds, which are particularly used in polyester fibers, have proven to be highly effective. Phosphorus compounds are slightly less harmful to the environment when released and are therefore often the first choice. Their effectiveness is based on the fact that they form a protective carbonization layer and intercept radicals, which reduces the flammability of the material. The release of toxic gases and further heat development is limited.
For several years now, there has been a shift in the use of synthetic fibers toward bio-based fibers. Although their market share is still small compared to established synthetic fibers such as polyethylene terephthalate or polypropylene, they are growing steadily. Bio-based fibers are gaining in importance because they reduce the demand for fossil raw materials. At the same time, their use supports the circular economy and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Persistent and effective flame retardancy in bio-based fibers that is also inexpensive and environmentally friendly could give bio-based textiles a boost in innovation and contribute to significant market expansion. This is where the DITF's “Polymers and Fiber Composites” research team comes in with the development of a flame-retardant, bio-based plastic called polyethylene furanoate (PEF). PEF is similar in many properties to the widely used polyethylene terephthalate (PET), but unlike PET, it is made from bio-based monomers. While PEF is already technologically advanced and on its way to the mass market, it currently lacks flame retardancy, which would enable its widespread use in the textile sector.
At the DITF, PEF is not only synthesized in in-house reactors. Extensive test series have also been conducted to evaluate the suitability of various phosphorus-based flame retardants in different concentrations. Two things are important to the researchers here: First, the flame retardant should be covalently bound to the polymer molecules to prevent bleeding. This is crucial for long-term fire protection of fibers because of their small diameter and high specific surface area. Second, the concentration of flame retardant should be as low as possible while still providing the best possible effect. Despite their good fire protection properties, all common additives share that they are potentially harmful to health and, when released into the environment, are difficult to degrade because they are chemically stable. In Denkendorf, they have not only succeeded in meeting these requirements. They have also been able to increase the molecular weight of the synthesized polymers by solid state polymerization to spin fibers with higher strength.
Further thermal and rheological investigations of the polymers with different flame-retardant concentrations identified the most suitable variant for the spinning process. In addition to the PEF variant containing five grams of phosphorus per kilogram of polymer in the form of copolymerized organophosphorus compounds, a flame retardant-free PEF reference was spun. The fibers obtained in the spinning laboratory were processed into textile fabrics, which were subjected to fire tests. The flame-retardant knitted fabrics showed significantly reduced flammability. The DITF will continue to study in flame-retardant, bio-based PEF fibers.
















