#Research & Development
New 3D printing process enables sustainable fiber composite components modeled on nature's example

We can take advantage of these principles to design and manufacture bio-based, sustainable fiber reinforced composites, which are currently in high demand. Bio-based fiber reinforced composites consist of natural fibers or cellulose fibers embedded in a bio-based matrix. The bio-based components offer properties comparable to those of commonly used glass fiber composites. The German Institutes of Textile and Fiber Research (DITF), together with Arburg GmbH + Co KG, are developing an energy- and material-efficient 3D printing process for manufacturing of such lightweight bio-based fiber composites.
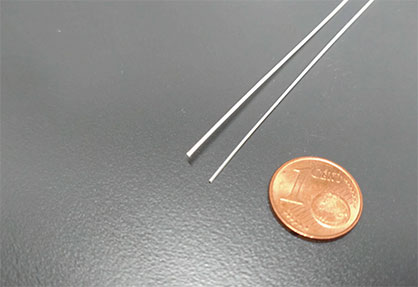
In fiber composites, which occur naturally, reinforcing fibers such as collagen or cellulose fibrils are embedded in a matrix of lignin, hemicellulose or collagen. The fiber strands align with the stress patterns. Tissues are formed mostly via solution-based physio-chemical processes that take place at ambient temperature. Similar to nature, new 3D printing processes with continuous fiber reinforcement also allow the deposition of fiber strands in the right place (topology optimization) and in the appropriate direction in accordance to the load. However, natural fibers such as cellulose fibers are sensitive to higher temperatures. Therefore, they cannot be processed in the commonly employed thermoplastic 3D printing process.
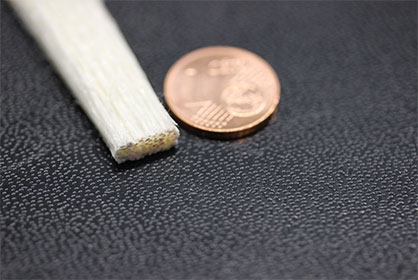
The result of the research work is 3D-printed fiber composite components consisting of cellulose continuous fibers embedded in a cellulose-based matrix. Newly developed 3D-printing process enables to manufacture the composites at ambient temperature. This means that - as in nature - the material and component can be produced simultaneously in a single operation at ambient temperature.
The cellulose fiber strand is first stabilized with a binder for processing in the printer. The specially designed print head transforms the binder into a matrix with which the cellulose continuous fibers are encased. Since the cellulose fibers and the matrix have similar chemical structures, the composite component is particularly stable. The mechanical properties, such as breaking strength, are exceptionally good. The solution-based and energy-efficient manufacturing method developed by the research team can also be used in other composite materials manufacturing processes. It is particularly suitable for processing temperature-sensitive materials that are in high demand, such as natural or cellulose fibers.
The " CellLoes-3D-Druck" research project is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research as part of the "Biologisierung der Technik" ideas competition.















