#Research & Development
Antiviral tests on protective clothing for infection control
Viruses can survive on plastic surfaces or textiles for several hours to days. These surfaces therefore play an important role in the transmission of viruses as pathogens. Numerous studies were done on this topic during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Textiles treated with antiviral agents can help to reduce this risk of transmission. This offers added value, especially for textiles used in medical environments.
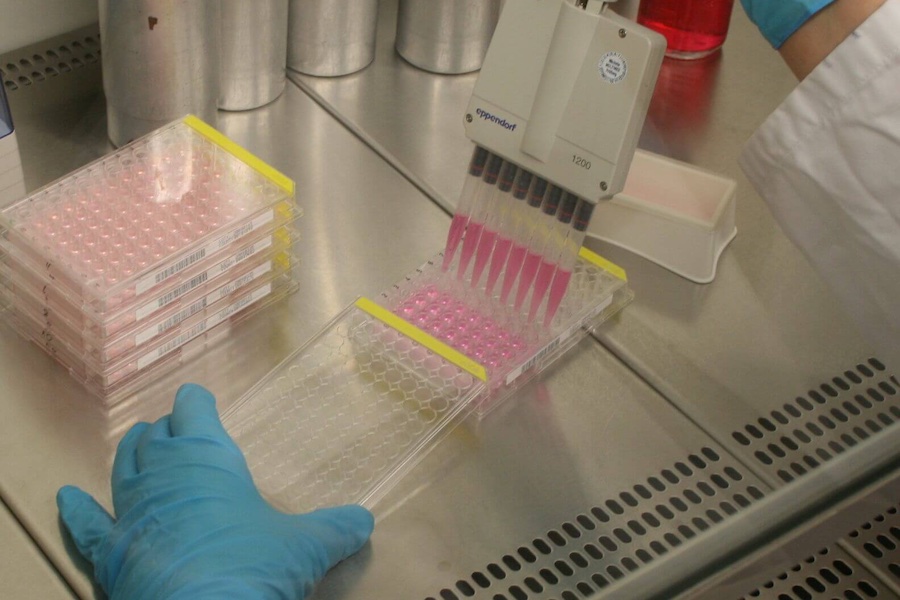
In order to confirm these antiviral properties, laboratory tests are the state of the art and help to minimize trials in a medical environment. However, working with viruses is very complex and elaborate, as viruses cannot be proliferated on culture media like bacteria. By definition, viruses are not living organisms because they are dependent on host cells to replicate. For laboratory tests, this means that both technical expertise in microbiology and in cell culture technology must be combined for successful work. For laboratory activities involving human and animal pathogens, official authorization is required. The DITF biological testing laboratory is authorized for work with pathogens in accordance with the German Infection Protection Act and the Animal Pathogens Ordinance up to risk group 2. These are microorganisms that can cause disease in humans or animals which can be well controlled generally.
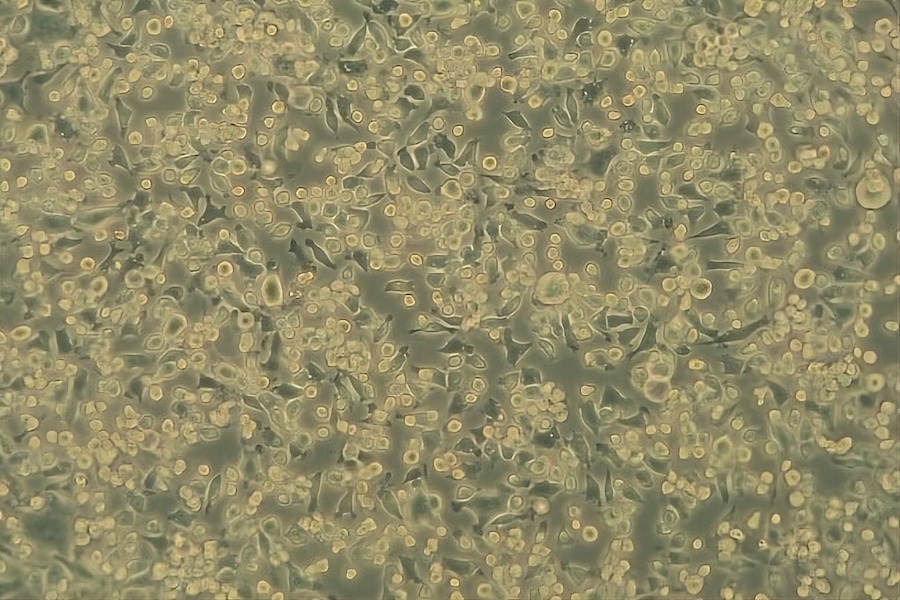
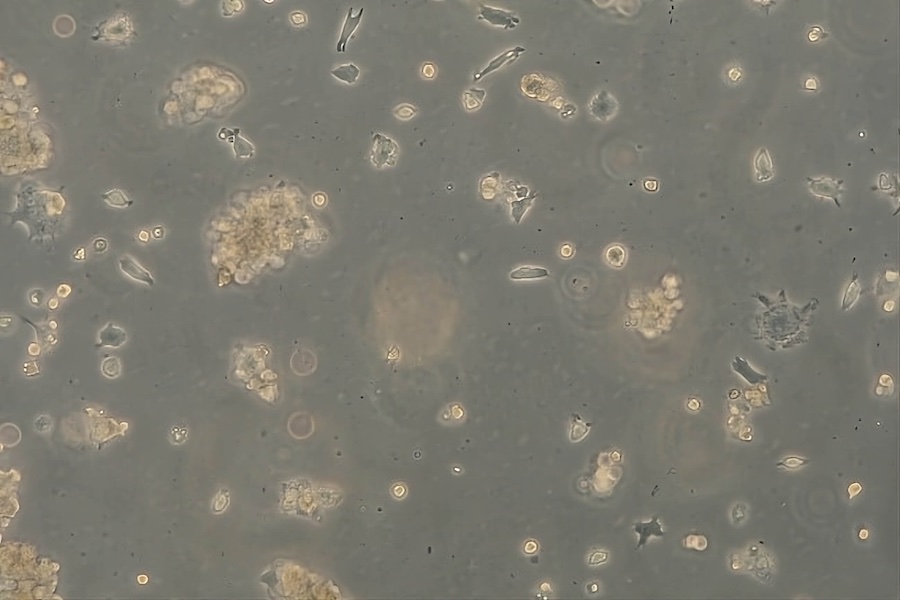
Usually test laboratories carry out antiviral tests with so-called bacteriophages because they are easier to handle. These viruses use bacteria as host cells to replicate. A different, more realistic approach was taken at the DITF as part of a research project. Here, antiviral activity was determined against a coronavirus. With the MHV virus, a corona virus was chosen that is genetically very closely related to the SARS-CoV-2 virus and uses eukaryotic cells as a host. Eukaryotic cells are cells with a nucleus such as those found in humans and animals. The test procedure for determining the antiviral efficacy against coronaviruses had to be adapted to both the viruses and the host cells. In case the host cells are infected by the viruses and used as a “replication machine”, these cells show damages, so-called cytopathic effects, which are clearly visible under the light microscope. The visible damages to the host cells are used to determine the number of viruses indirectly as they are not visible under the light microscope due to their very small size.
As part of the joint research project with Heraeus Precious Metals GmbH & Co. KG to develop antimicrobial protective clothing for infection control based on AGXX® technology, a test protocol was developed at the DITF biological laboratory to determine the antiviral activity against a coronavirus. A significant inactivation of MHV coronaviruses of more than 99 percent was demonstrated in textiles finished with AGXX®. The tests on the antiviral properties of textiles against a coronavirus make an important contribution to the development and quality control of antiviral textiles.

















