#Research & Development
Latent epoxy systems for fiber-reinforced plastics
New resin systems enable simplification of process technology
However, the special properties of FRP have so far been offset by relatively high production costs due to the complex manufacturing processes involved. Low raw material costs and low-cost production techniques are necessary to establish FRP in industrial series production on a large scale. These have to be designed in such a way that they enable the production of components of high and, above all, constant quality – require-ments which are not always easy to meet, especially for large components such as rotor blades of wind turbines.
Established systems with many disadvantages
In the processing of established thermoset two-component epoxy systems, some difficulties have to be handled to reach these objectives. For example, reaction accelerators are usually added to epoxies, which cause faster curing and thus a more cost-effective production. However, the resins in this form are difficult to store and transport: Due to the reaction accelerators they behave very reactive and therefore have to be cooled in a defined way with high equipment efforts until processing.
In established two-component epoxy systems, resin and hardener are mixed directly before processing. During processing, cross-linking takes place within a short period of time. There is a risk of pre-crosslinking, which starts before the textile layers are com-pletely penetrated by the resin. If this process is not perfectly coordinated, materials with non-infiltrated areas are obtained which are of inferior quality. Air inclusions can also occur during the mixing of resin and hardener, which can only be reduced by complex venting techniques of the epoxy system.
To reduce the effort of these demanding process techniques was the goal of a research project at the DITF Denkendorf, which deals with the optimization and establishment of so-called latent epoxy systems. In such systems, resin and hardener can be present in a mixture already ready for use (single-component system). Although this mixture is highly reactive, the polymerization cannot start uncontrolled and prematurely because the reaction-initiating pre-catalyst used is chemically protected. The resin system is storable and of constant viscosity, which is a considerable advantage for the infiltration process. The viscosity can even be reduced during processing by adding heat, so that bubble-free infiltration of the textile layers is even more possible. The catalyst is only activated at a defined temperature after the infiltration is completed and then initiates a fast and complete polymerization of the epoxy resin.
Single-component systems are in principle already commercially available. In these, however, the hardener component of the epoxy system is only inhibited. However, these systems do not show complete latency, since they can be activated over a wide temperature range and a slow cross-linking reaction starts just above room temperature.
The systems developed at the University of Stuttgart, Institute of Polymer Chemistry (IPOC), Chair of Macromolecular Materials and Fiber Chemistry and the DITF, on the other hand, are characterized by complete latency: The single-component system of resin and hardener is completely stable over a wide temperature and time range and has a constant viscosity.
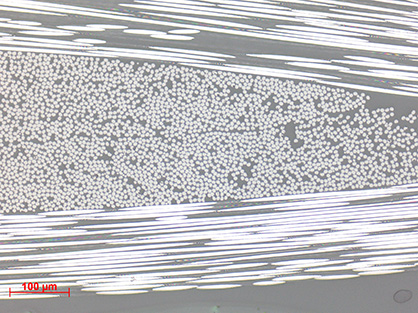
The advantages of the newly developed single-component epoxy system are primarily the possibility to infiltrate even large components with consistent quality and to implement a subsequent polymerization precisely, quickly and thus practically in serial production. The components can be manufactured with constant quality. Air inclusions can be almost completely avoided. The process-technical advantages include the fact that no mixing technology is required for the resin system and that the single-component resin systems can be stored and transported easily and safely.
Within the framework of the research project, latent single-component epoxy systems were brought to such a high level of development at the DITF Denkendorf that they are now mature for serial, industrial production. Due to the cost savings in process technology, the financial obstacle for the processing of FRP by small and medium-sized companies can be overcome more easily.















